Assigning internal and external hardware controls adds a whole new dimension of control and musicality to KR-55C, and it's really easy to do. The MIDI Tab is where all controller assignments can be viewed and tweaked - it can be opened by clicking the MIDI logo button in the top purple menu strip.

First we'll show how to assign an external hardware controller to a KR-55C control, then we'll go over all parameters in the MIDI Tab.
Basic External Hardware Control Assignment
This is the quick, "I just want to assign a hardware control right now!," section. We recommend reading this whole section to best take advantage of MIDI control assignments.
In this example, we’ll assign a hardware slider/knob control to the Snare Drum Decay knob. Begin by opening the Instrument Edit page by clicking the Inst button under Edit Mode in the top-right corner.

In the Snare Drum section, right-click on the Decay knob, and select MIDI Learn in the popup menu.
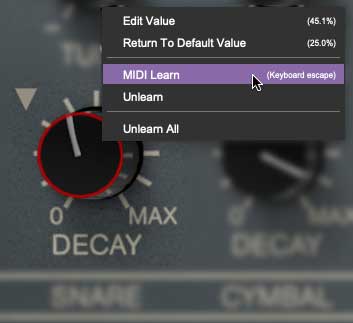
A transparent purple overlay appears over the slider indicating that it's in learn mode. Now move the desired hardware control device. The purple overlay disappears and the hardware control will move the Decay slider. If you get cold feet (or accidentally put the wrong control into learn mode), learn mode can be aborted by right-clicking and selecting Stop Learning or thwacking the [ESC] key.

This is the basic procedure for assigning hardware controllers to any KR-55C control.
Once a MIDI controller has been assigned, in addition to real-time control of any parameter, you’ll also be able to record and play back controller data from a DAW.
The MIDI Tab
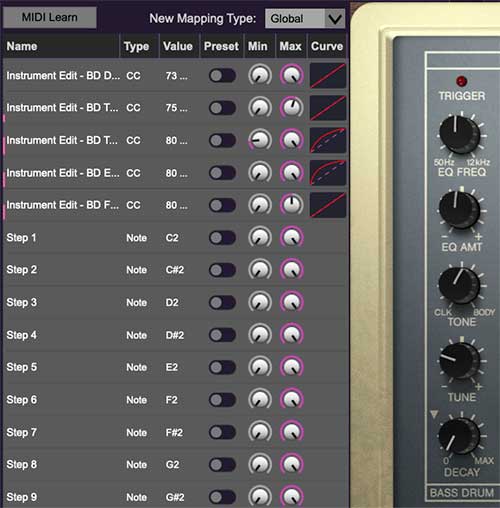
This is command central for all MIDI controller assignments. Here you’ll be able to fine-tune and see information about all currently assigned controllers.

To view or hide the MIDI Tab, click the MIDI button in the purple top toolbar.

MIDI Learn button- This is almost exactly the same as enabling MIDI learn mode by right-clicking a control. Click the MIDI Learn button to enter learn mode (all controls turn purple). Unlike right-clicking on specific controls, where KR-55C automatically exits controller assignment mode, clicking the MIDI Learn knob "stays on" to enable assignment of multiple hardware controls. This lets you assign a gaggle of controls in one swell foop.
To assign multiple controls, click MIDI Learn, click an onscreen control, move the desired hardware knob or slider, continue clicking and assigning on-screen controllers until all desired controls are assigned, then click Stop Learning to exit learn mode.
Remember that a single hardware knob/slider/button isn't limited to controlling just one parameter - a single hardware controller can be "multed" to operate as many controls as you'd like.

New Mapping Type- This popup menu selects whether newly assigned MIDI mappings will be global (affects all sounds and doesn't change when different presets are selected) or saved with individual presets.
MIDI Tab Columns
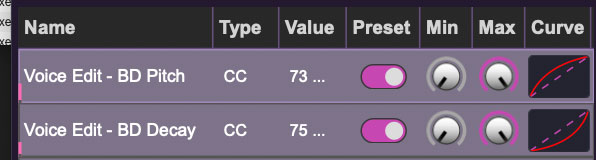
Name- Displays the name of the parameter being controlled.
Type- There are five possible types of controller automation:
Note- Notes played on a MIDI keyboard controller, expressed as C-1 to G9
CC (MIDI Continuous Controller)- The standard 128 MIDI controller numbers as defined in the MIDI spec. More specifically, these are the controllers transmitted by hardware knob and slider controls. MIDI CC’s can be used to control parameters in real-time or recorded and played back within DAW software.
MMC (MIDI Machine Control)- The MIDI control protocol for tape machine-style transport controls. Back in the dark ages, this was used to control wonky old Tascam and Fostex reel-to-reel monsters, but it's useful if your MIDI controller has tape-style transport control buttons.
Aftertouch- Besides sounding like a 1981 Melissa Manchester record, some keyboard controllers transmit controller data when keys are pressed and released as they're held down. The vast majority of keyboard controllers with aftertouch transmit "mono" aftertouch only; in other words, aftertouch data is the sum of all keys to one single data stream.
Key- This allows keys of the computer QWERTY keyboard to at as button controls for onscreen controls.
Value- Displays the specific automation controller. In the case of a Note this would show a MIDI note number (C-1 to G9, for a MIDI CC, this would be the MIDI CC controller number, etc. Clicking on the value opens a pop-up menu where all values are displayed and can be selected.
Preset- This slider works in conjunction with the New Mapping Type menu. In the left position (gray background), the MIDI mapping is global (affects all sounds and doesn't change when different presets are selected), in the right position (lavender background), the MIDI mapping is saved with, and only affects the current sound preset.
The Preset switch is super nifty, because it means MIDI mappings can easily be set to global or per-preset status at any time.
Min- Sets a limit on the lowest value any automation control can set a mapped controller to. This actually recalibrates the range of the automation controller to the remaining parameter range.
Max- Sets a limit on the highest value any automation control can set a mapped controller to. This actually recalibrates the range of the automation controller to the remaining parameter range.
Super Tricky Min-Max Tricks- Not only can parameter ranges be limited via the the Min and Max knobs, mapped control destinations can be completely inverted by setting the Min knob all the way up and the Max knob all the way down (or anywhere in between).
Limiting and inverting parameter ranges with the Min/Max controls is particularly useful when multiplexing a single hardware control to operate multiple parameters. Along with the Curve control, the customization possibilities are super flexible.
Curve- These allow the customization of how incoming MIDI CC controls affect the movement of onscreen controls, ranging from exponential to linear to logarithmic curves.
MIDI Tab Column Configuration Right-Click Menus
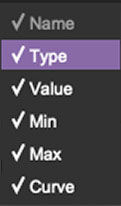
Right-clicking anywhere in the top row (Name, Type, Value, etc.) displays the column configuration menu. Checking/unchecking these allows hiding and display of each column. This has no effect on assignments.
MIDI Tab Parameters Right-Click
Right-clicking on an assigned parameter opens the menu above.
MIDI Learn- This is used to change the controller assigned to a particular parameter.
Unlearn- Deletes the selected automation parameter.
Unlearn All- Deletes all controller assignments for the patch. A warning dialog pops up prior to deletion in order to thwart potential unlearn-related disasters.
MIDI Controller Suggestions
Following are some MIDI controller assignments we find particularly useful:
Assigning button controllers to the Panel Mode Main, Voice Edit, and Effects/Mixer select buttons lets you rapidly switch between KR-55C's three UI windows. Note that the QWERTY keypad 1/2/3 keys are already hardwired this way when using the standalone version of KR-55C. You can do the same when using KR-55C inside a DAW. The only caveat to using QWERTY keys within a DAW is that some DAWs get finicky about QWERTY key priority with plugins (and by "some," we mean Logic...).
Similar to above, assigning button controllers to the Mixer Mute buttons makes it easy to experiment with muting instruments. This is a nice way to get a lot of mileage out of the factory preset rhythms.
Try assigning a button or any keyboard controller key to the Inst Trigger button when creating patterns in User mode. This is nice, because KR-55C "records" hits into the current pattern while in play mode.